PREREQUISITES
The ability to edit permissions on the domain. You may need the help of your local IT professional.
INTRODUCTION
As of version 3.3, EDL is now a Windows Service that runs regardless as to whether or not the PC on which it is running is logged in. There are numerous good reasons for this, but one of the trade offs is that a Windows Service runs under a different security context than regular applications. As such, there are different security considerations when it comes to setting up EDL to run on your network.
Let's assume you want to run EDL on an application server (\\appserver1). It will look for QCC files on a file server (\\fileserver1) and place the results into a SQL Server database.
By default, the EDL Load Service is installed and told to use "Network Service" as an account. This is a special Windows account (with no password) that gives the EDL Load Service general access to the network as if it was in the "Users" group. The Users group is another Windows built-in group. Under normal circumstances this should work without an issue. However, in certain cases IT will lock down access to the Network Service account for security reasons. If this is the case, you will need to create a separate functional ID that EDL can use to access the QCC files on your file server.
RULES
- Services cannot used mapped letter drives for network resources. You can use letter drives for the C drive and other local resources, but mapped network resources will not work. This is because a service uses a separate log in context that does not map drives. This is even true if you enter your own login credentials. Even though you have an M drive, the service will not. Instead use UNC style paths to get to your network. The format is always "\\servername\shared directory\folder\folder\folder\etc. For example: \\fileserver1\D-Drive\Prolink\
- Do NOT use your own or any person's user id. If you do and change your password at some point, EDL will not know the new password and will stop working. It is much safer to create a special user account for EDL that does not have an expiring password so you do not have to troubleshoot later.
STEPS
- Have your IT department create a special user id for EDL that does not have an expiring password.
- Have your IT department give Read/Write (modify) access for this user to the network path(s) where your QCC files are stored. This will typically entail creating a group with access and adding the user to the group.
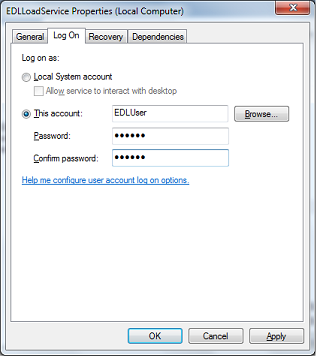
- Set the EDL Load Service to use the login id you just created in Step 1.
- Go to Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services
- Right click on EDL Load Service and choose Properties.
- Click the Log On tab.
- Choose This Account, type the logon, type the password twice, and click Apply.
- Click OK.
- Restart the service by right clicking on it again and choosing Restart.
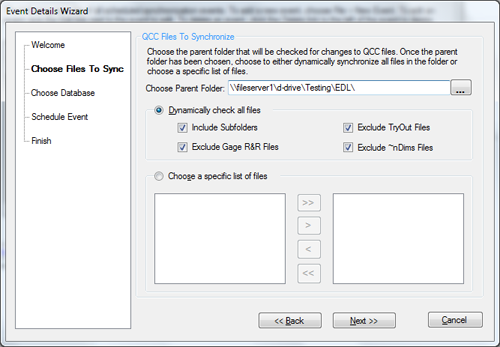
- In the EDL event, make sure to specify the appropriate path using the UNC format.
NOTE: Just because you can see the files below in the list does not mean the service can see them. Remember that you are running the EDL client under your credentials.
That should be all you need.
MORE INFORMATION
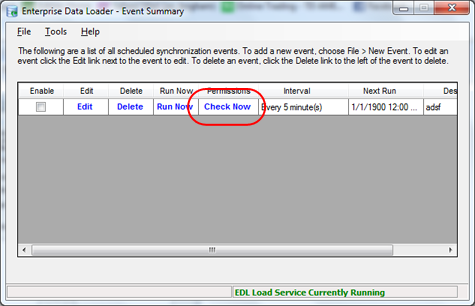
To test the credentials of a particular event, you can use the Check Now link on the main EDL screen. When you click this link, you will see a Permission Check Utility screen appear. At that point, the EDL Client will send a message to the EDL Load Service asking it to look at the QCC file directory for that particular event. The service will respond by reporting every file it finds in that directory. If you do not see any results in a couple of seconds then you know there must be a permission problem with the network location and the account being used by the EDL Load Service. If you see results then it means the service should load the QCC files into the SQL database properly.